HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
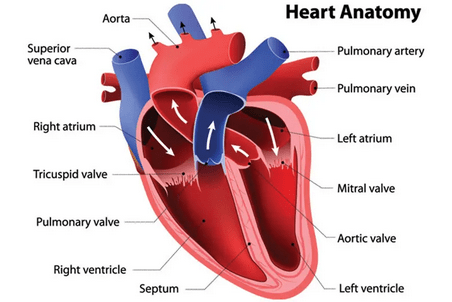
Seven Early Signs You Are Prone To Heart Attack
Continue Reading
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
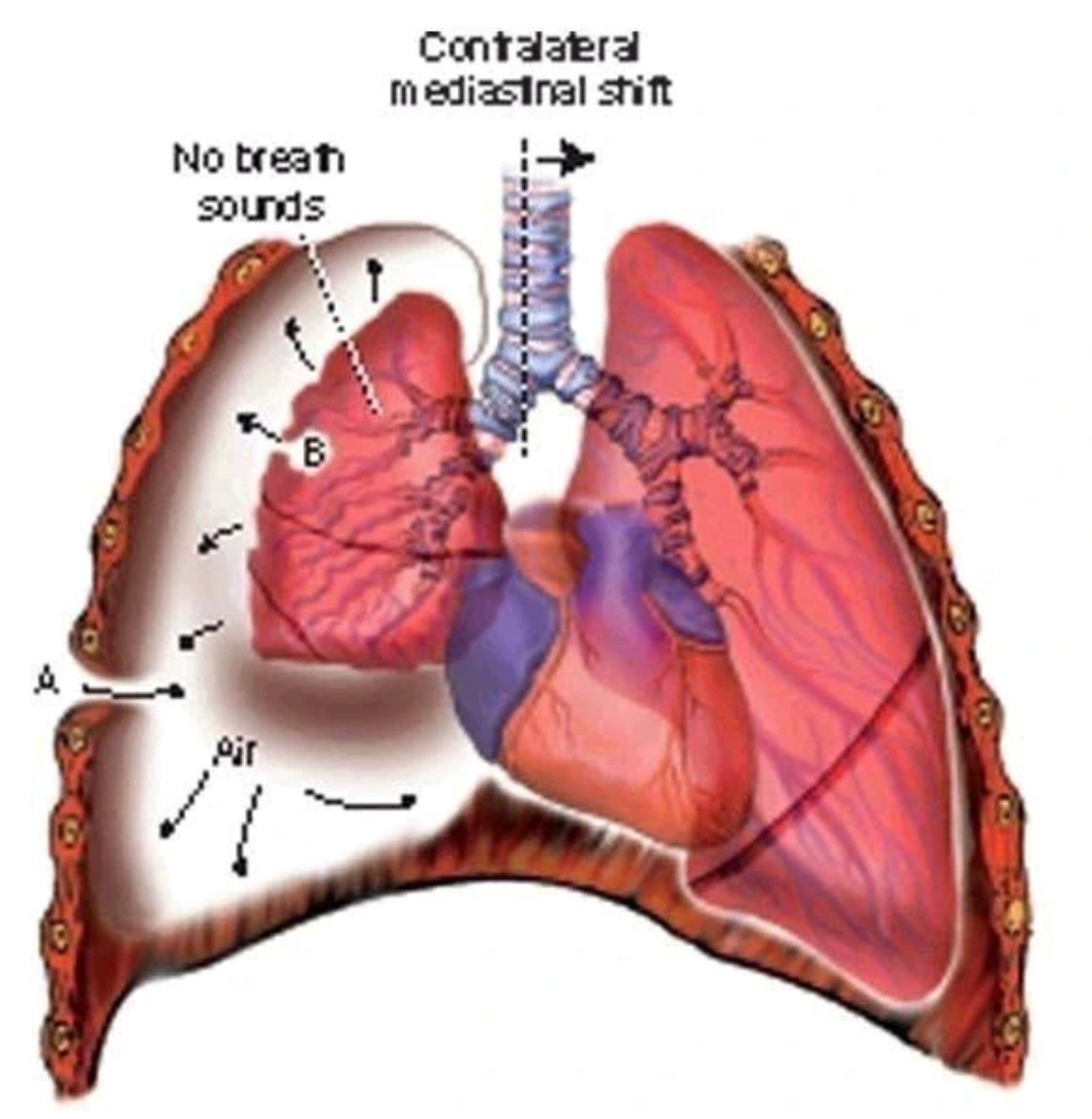
Your Lungs Are Not In Good Condition if You Experience the Following
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
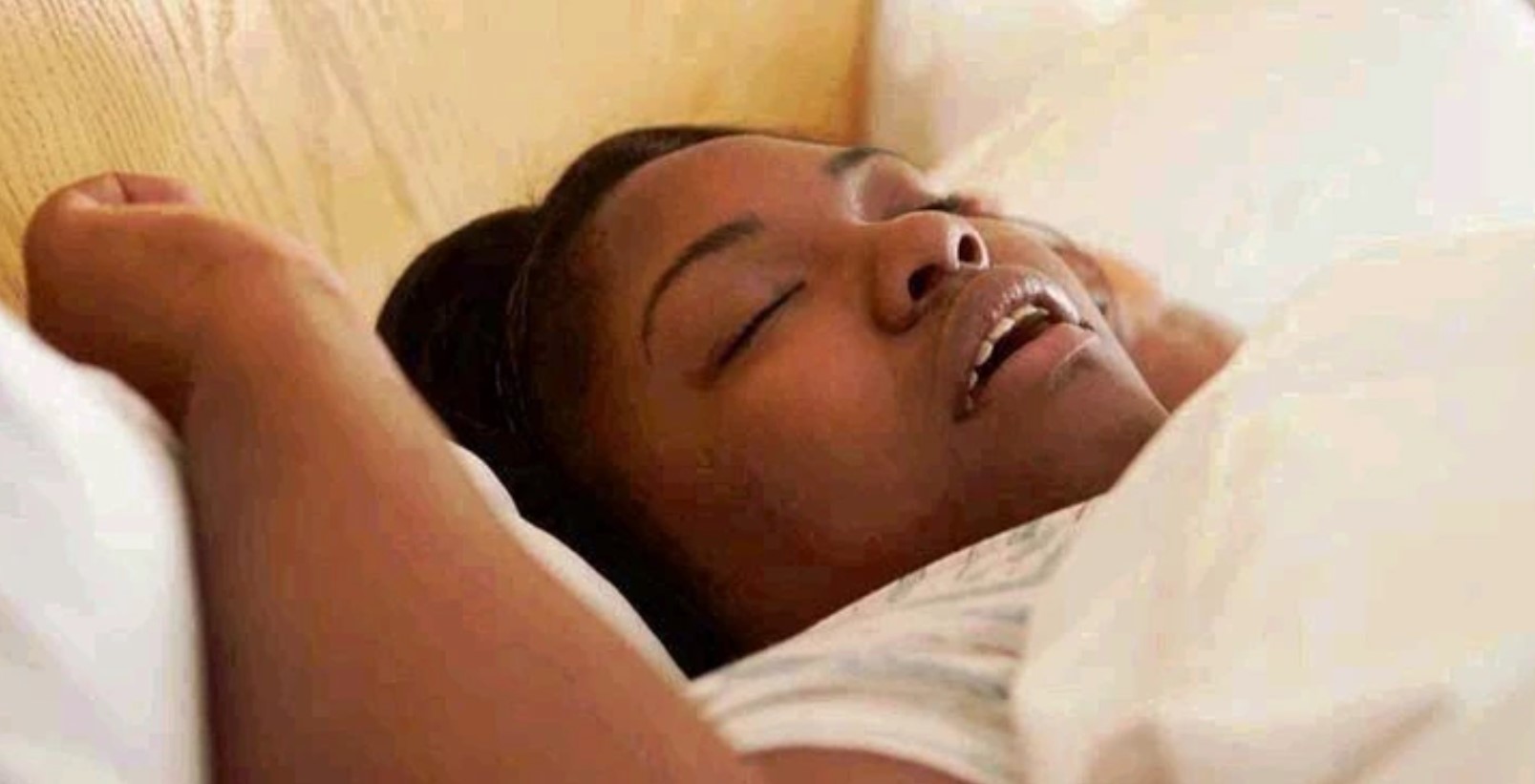
4 Major Reasons Some People Die In Their Sleep
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
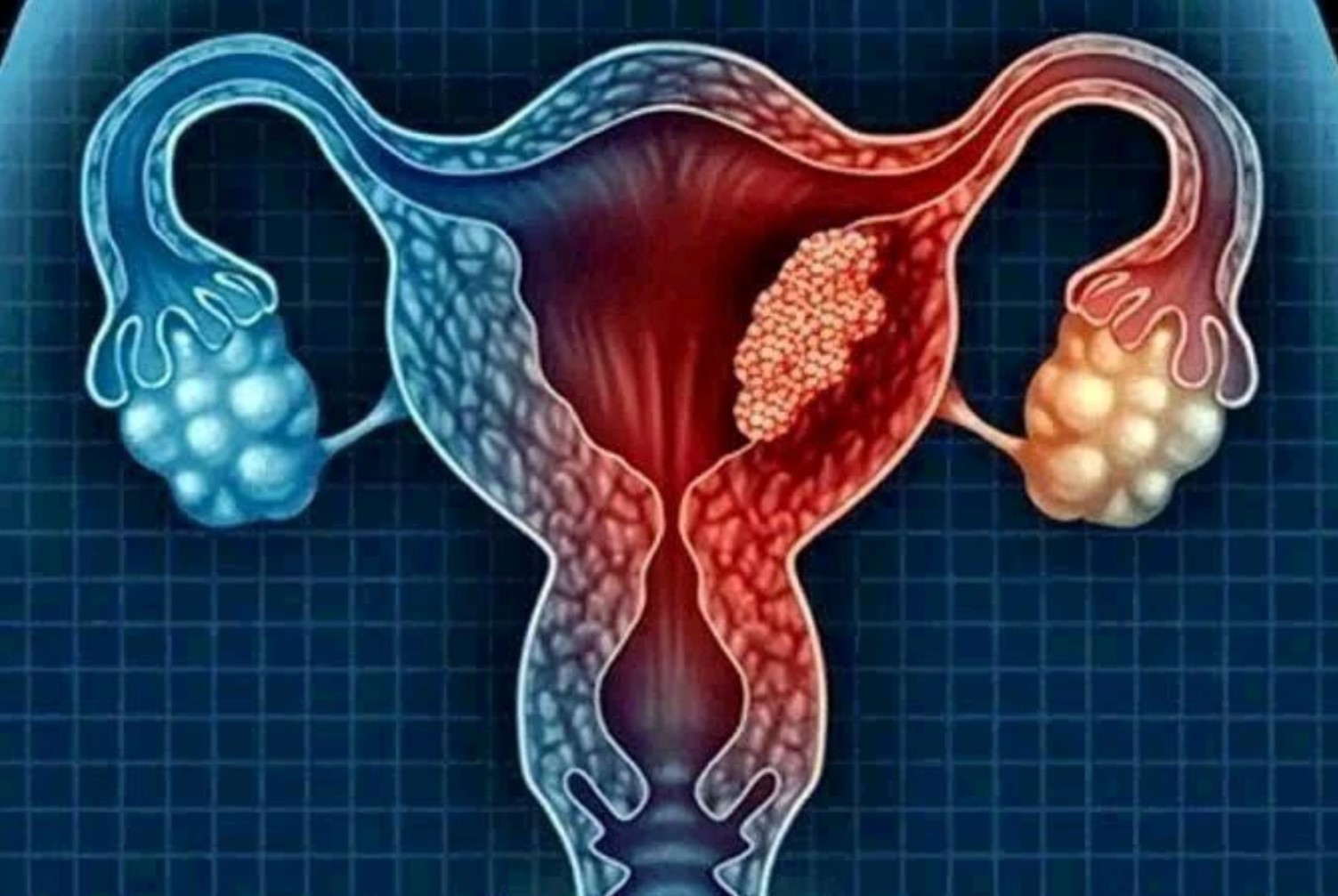
Uterine Cancer: Stay Away From These 4 Things To Avoid The Risk Of Being A Victim
-

 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months agoOndo Govt Reacts As Court Nullifies 33 LCDAs Created By Late Akeredolu
-

 SPORTS7 months ago
SPORTS7 months agoYoung talent wins big – Archysport
-

 METRO10 months ago
METRO10 months agoMom gave birth to quadruplets, the doctors and nurses in the room could not believe what they saw!
-
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoSingle-A Carolina League, U.S. Match Rankings and Results: Recent Updates
-
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months agoFoods That Cause Stomach Cancer: What to Avoid for a Healthier Life
-

 METRO7 months ago
METRO7 months agoThis Innocent Man Was Wrongfully Jailed. What He Did Next Will Make You Cry! –
-

 IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS10 months agoTourist ignores wa:rnings, gets bitten by King’s Guard horse
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoFrance wins on penalties against Portugal