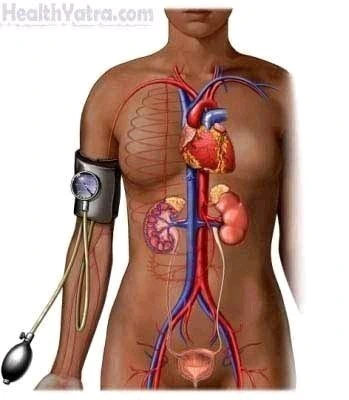
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition where the force of blood against the walls of arteries is consistently too high. This condition is often asymptomatic in its early stages, earning it the nickname “silent killer,” as it can quietly damage organs over time. However, as blood pressure levels rise, symptoms may become noticeable, indicating potential complications and the need for medical attention…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
Early Symptoms:
1. Headaches: Persistent headaches, especially at the back of the head, can be an early indicator of high blood pressure. These headaches may be more severe in the morning.
2. Vision Problems: Blurred or double vision, and even sudden visual disturbances, can occur due to hypertension affecting blood vessels in the eyes.
3. Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or lightheaded, especially when standing up quickly, can signal that blood pressure levels are elevated.
Advanced Symptoms:
1. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity or when lying flat, may indicate that hypertension is affecting the heart and lungs.
2. Chest Pain: Chest pain can occur when high blood pressure leads to heart muscle strain or reduced blood flow to the heart (angina).
3. Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or fatigued, even after adequate rest, can result from the heart working harder to pump blood against elevated pressure levels.
4. Irregular Heartbeat: Arrhythmias or palpitations may occur as the heart responds to increased pressure and strain.
Severe Symptoms (Hypertensive Crisis):
1. Severe Headaches: Intense headaches that do not respond to usual pain relief medications can indicate a hypertensive crisis, requiring immediate medical attention. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
2. Nosebleeds: While common in movies, nosebleeds are less common with hypertension and usually indicate severely elevated blood pressure levels.
3. Severe Anxiety or Shortness of Breath: Panic-like symptoms can occur during a hypertensive crisis, along with significant shortness of breath.
Long-Term Complications:
Untreated or poorly managed hypertension can lead to serious health problems over time, including:
– Heart Disease: Increased risk of heart attack, heart failure, and thickened heart muscle (left ventricular hypertrophy).
– Stroke: Elevated blood pressure can lead to the narrowing and weakening of blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
– Kidney Damage: Chronic hypertension can damage the kidneys’ blood vessels and reduce their ability to function properly.
– Eye Damage: Hypertension can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
Conclusion:
Recognizing symptoms of high blood pressure is crucial for early intervention and management. Regular blood pressure monitoring, especially for individuals with risk factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, or a family history of hypertension, is essential. Lifestyle changes, including maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, reducing sodium intake, and managing stress, can help prevent and control high blood pressure. Medical treatments, such as medications prescribed by healthcare providers, are also effective in managing blood pressure levels and reducing the risk of complications.

 SPORTS9 months ago
SPORTS9 months ago
 SPORTS9 months ago
SPORTS9 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months ago
 METRO9 months ago
METRO9 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 METRO5 months ago
METRO5 months ago