HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
What Causes Too Much Mucus In Your Throat And What To Do About It

Continue Reading
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
5 Secret Benefits Of Adding Salt To Bathing Water
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
7 things that will make you look younger than your age
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
What Happens When You Eat a Banana First Thing In The Morning?
-
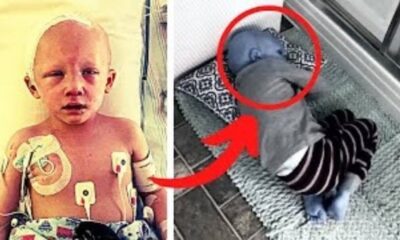
 METRO10 months ago
METRO10 months agoHeartbreaking Final Words of a Brave 4-Year-Old Boy Will Leave You in Tears!
-

 IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS10 months agoPresident Tinubu Re-elected ECOWAS Chairman
-

 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months agoParents, If You Want Your Child To Be Intelligent, Start Feeding Them These 8 Foods
-

 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months agoҚазақстанда 2025 жылдан бастап жасөспірім қыздарда генетикалық аурудың бар-жоғы тексеріледі
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoUnveiling Experience: The Spanish Men’s Basketball Team Prepares for Olympic Debut in Paris 2024
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoIn Brazil they talk about the cat’s curse: why they attribute the negative streak of the National Team to a feline
-

 SPORTS11 months ago
SPORTS11 months agoJJ Redick Named New Lakers Coach: A New Era Begins
-

 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months agoРесейде ер адам ұлының қуыршақ ойнағанына ашуланып, балабақша қызметкерлерін өлтіремін деп қорқытқан (видео)



