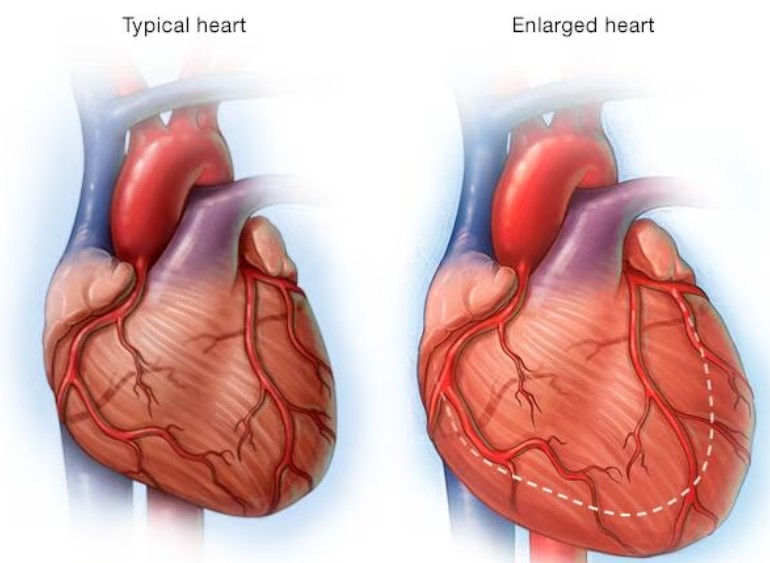
An enlarged heart, or cardiomegaly, is a condition where the heart becomes larger than normal. It can be a sign of various underlying health issues and can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Understanding the causes and signs of an enlarged heart is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
**Causes:**
1. **Hypertension (High Blood Pressure):** Chronic high blood pressure forces the heart to work harder to pump blood. Over time, this extra workload can cause the heart muscle to thicken or the heart chambers to enlarge. This condition is known as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
2. **Heart Valve Disease:** Valvular heart diseases, such as aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation, can lead to an enlarged heart. When valves don’t function properly, the heart must work harder to maintain blood flow, which can result in an enlarged heart over time.
3. **Cardiomyopathy:** This group of diseases affects the heart muscle. Types of cardiomyopathy include dilated cardiomyopathy, where the heart’s chambers enlarge and weaken, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick.
4. **Coronary Artery Disease (CAD):** CAD can lead to heart enlargement as a result of the damage caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to weakened heart function and potential enlargement.
5. **Congenital Heart Defects:** Some people are born with structural heart abnormalities that can cause the heart to enlarge as it tries to compensate for the defect.
6. **Heart Failure:** Both acute and chronic heart failure can cause the heart to enlarge. In heart failure, the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently, leading to compensatory enlargement.
7. **Fluid Retention:** Conditions causing excessive fluid retention, such as kidney disease or certain infections, can lead to an enlarged heart as the heart struggles to manage the increased fluid volume.
**Signs and Symptoms:** READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
An enlarged heart may not always present noticeable symptoms, especially in its early stages. However, common signs include:
1. **Shortness of Breath:** Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or when lying flat, can indicate heart enlargement and reduced heart function.
2. **Fatigue:** Persistent tiredness and weakness can result from the heart’s diminished ability to pump blood effectively.
3. **Swelling:** Edema in the legs, ankles, or abdomen can occur as a result of fluid buildup due to an enlarged heart.
4. **Palpitations:** Irregular or rapid heartbeats can be a symptom of an enlarged heart.
5. **Chest Pain:** Pain or discomfort in the chest can sometimes be associated with heart enlargement, particularly if it is related to underlying heart disease.
6. **Frequent Urination at Night:** This can be a sign of fluid buildup and congestive heart failure associated with an enlarged heart.
Diagnosing the cause of an enlarged heart typically involves medical history, physical examination, imaging tests such as echocardiograms or MRIs, and other diagnostic evaluations. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause to prevent further complications and manage symptoms effectively.

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE6 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE6 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE11 months ago
 METRO11 months ago
METRO11 months ago
 METRO6 months ago
METRO6 months ago