HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
Diseases That Can Be Cured By Eating Maize Without Beans

Continue Reading
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
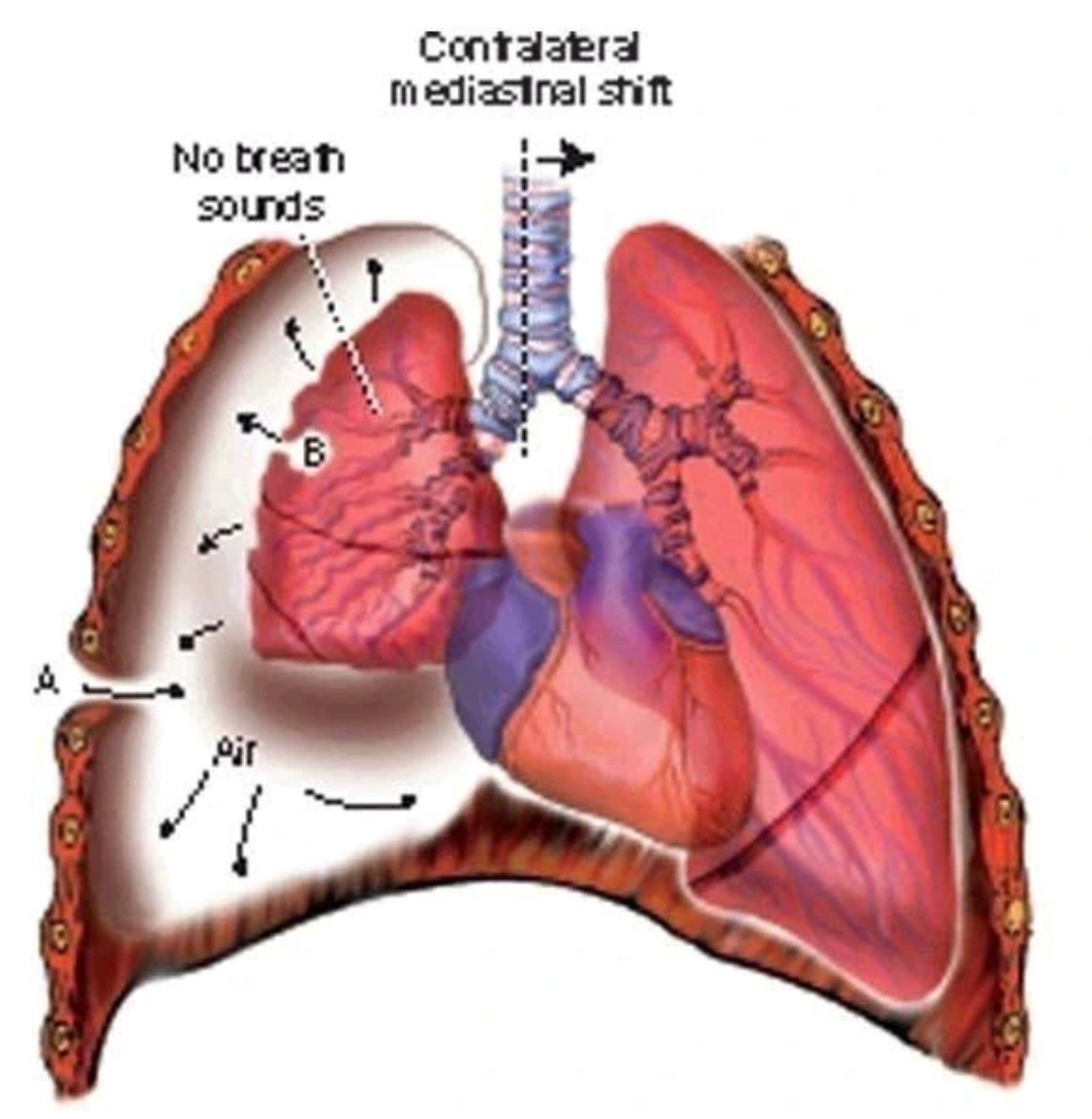
Your Lungs Are Not In Good Condition if You Experience the Following
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
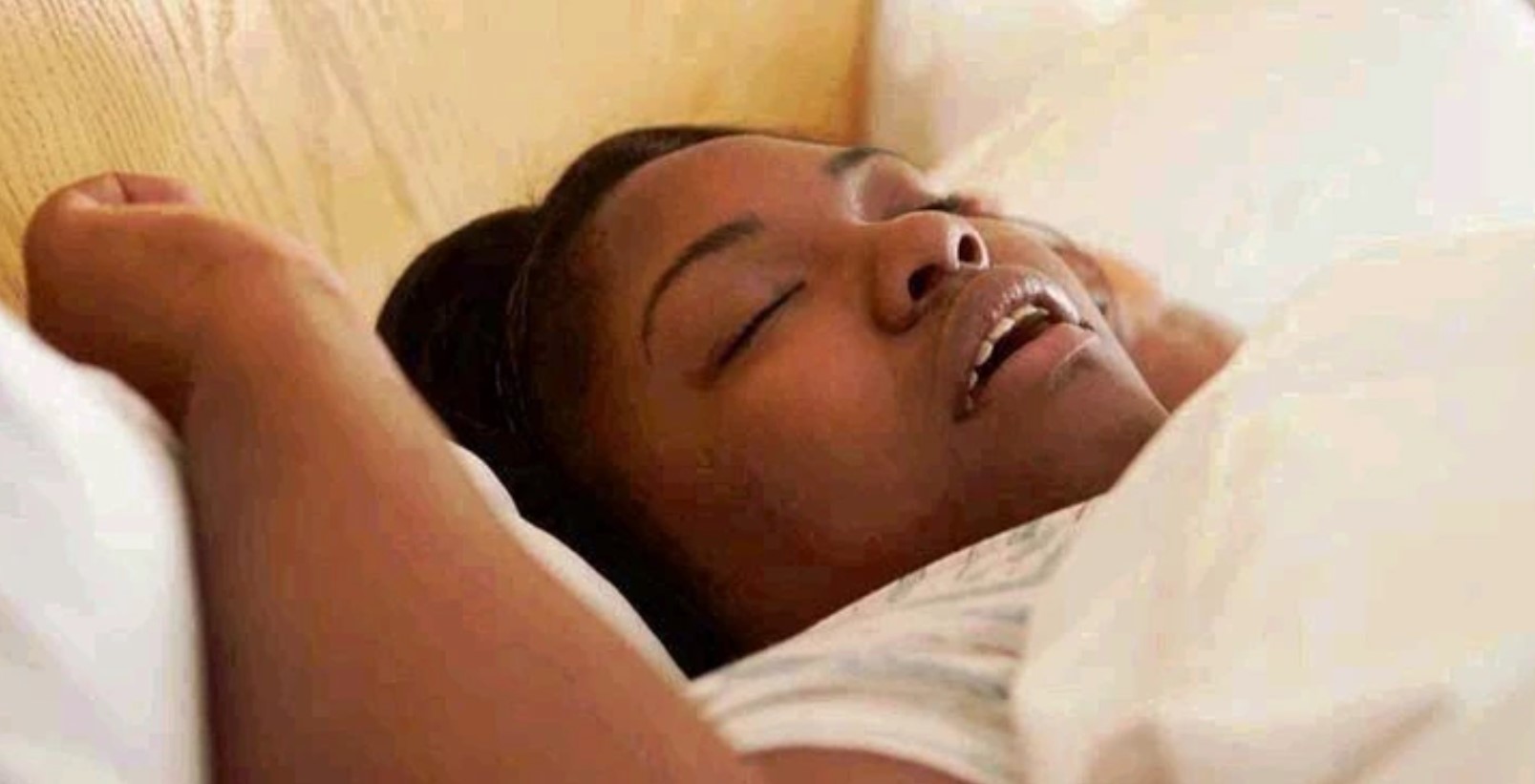
4 Major Reasons Some People Die In Their Sleep
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE
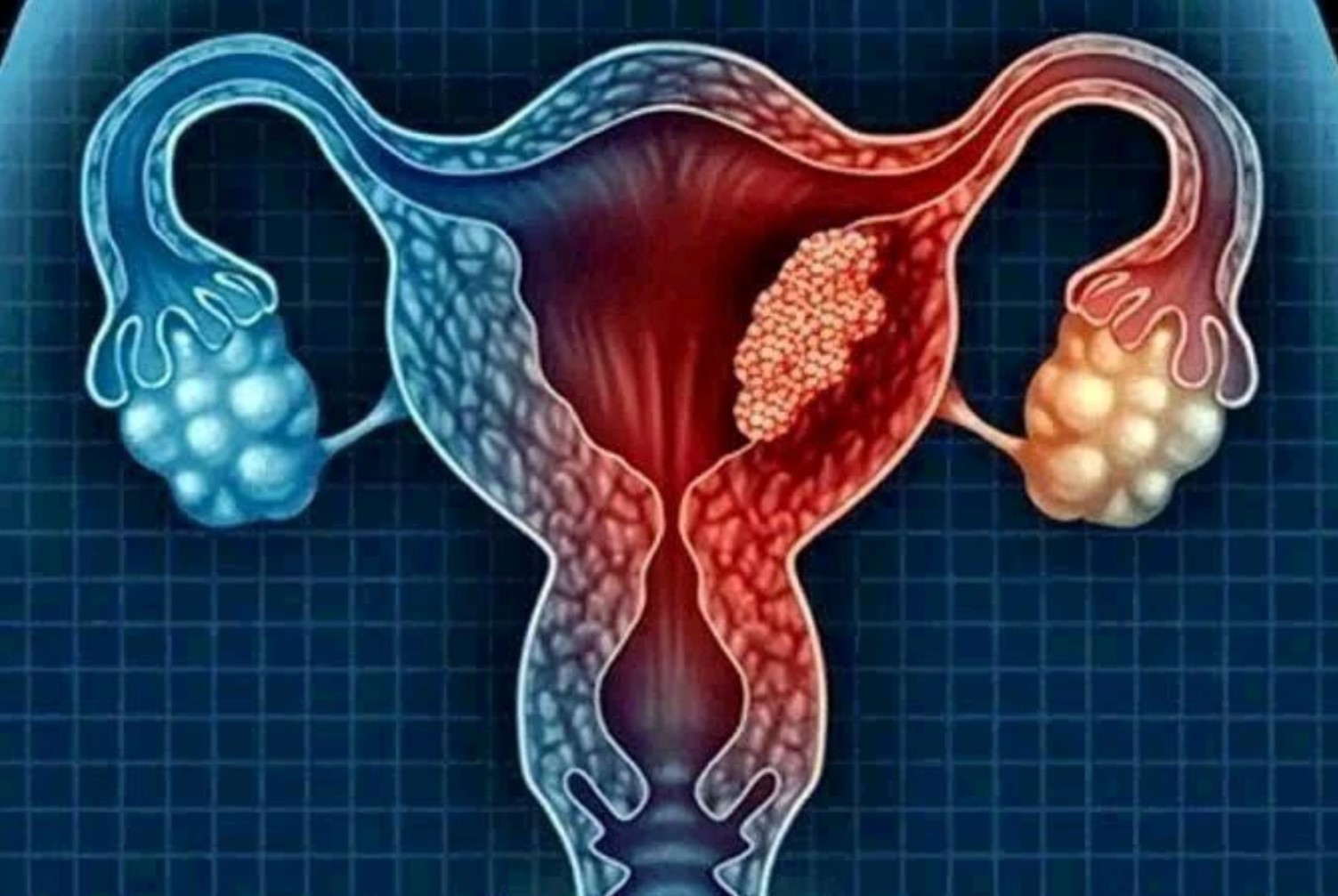
Uterine Cancer: Stay Away From These 4 Things To Avoid The Risk Of Being A Victim
-
 METRO10 months ago
METRO10 months agoMan gropes and harasses women outside club, doesn’t realize ‘one important thing’ until it’s too late!
-

 METRO11 months ago
METRO11 months agoWhen her son needed a friend, this dog’s reaction brought the mother to tears
-

 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months agoBereke Bank өз брендінің туған күнін атап өтуде!
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoBraving the Heat: Emma Marrone’s Fans Camp Out for Front Row Seats at the Ivan Graziani Amphitheater
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoDouble Match Report: Ferrara Baseball vs Shark Brothers at Ebl Championship
-

 METRO11 months ago
METRO11 months agoHow Long Do Eggs Last in the Refrigerator? Everything You Need to Know.
-

 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months agoКүдіктілердің туыстары Шерзаттың әкесін жауапқа тартуды сұрады (видео)
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoUncertainty at Bayern Campus: Halil Altintop’s Departure Looms as Markus Weinzierl’s Future Hangs in the Balance