With regards to being a woman, something that is generally vital to us is our body, and we make every effort to keep it flawless and immaculate consistent. With regards to being a woman, our bodies are something that means quite a bit to us. Each lady has a similar desire: to have a body that she can be pleased with, and to have the option to say that she is calm in her own skin. This is a general objective for all ladies…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
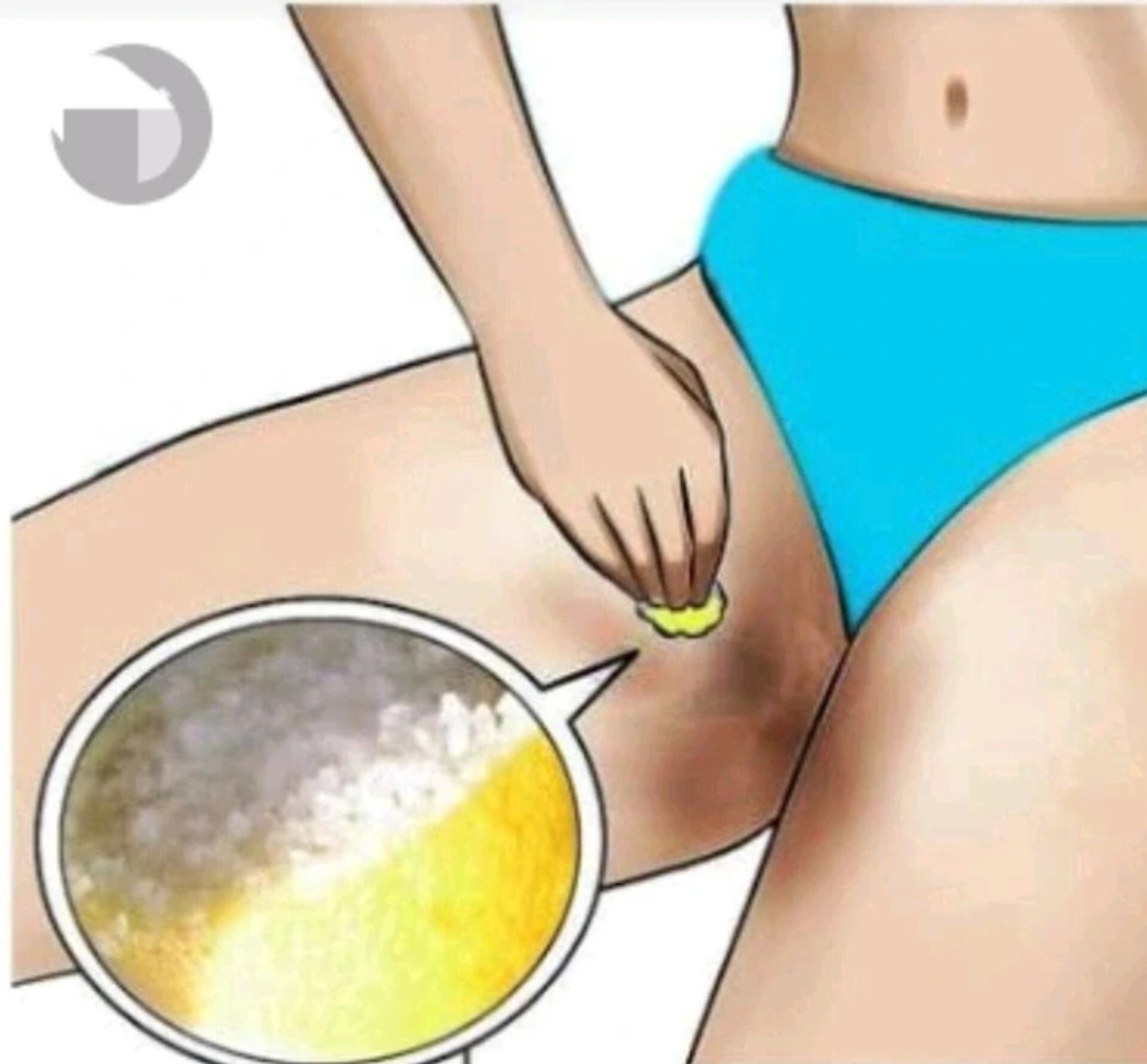
At the point when individuals come to see us, the most well-known issue they have is that they have dull inward thighs or a dim swimsuit line, the two of which can rather humiliate. We can treat both of these issues. As an immediate consequence of this, numerous ladies have created sensations of disquiet, and subsequently, they continually want to disguise themselves. As an immediate result of this, numerous ladies have created sensations of disquiet.
1. In the event that you are overweight, you have a more serious gamble of creating dim inward thighs due to the expanded contact that happens between your laps. The skin obscures because of the erosion, which is the justification for this peculiarity.
2. An adjustment of the shade of the skin might happen because of inordinate perspiring, especially when this condition is joined by the wearing of cumbersome dress.
3. Since over-shaving can cause staining, you ought to attempt to try not to do it in that specific region and on second thought utilize a hair evacuation treatment all things considered.
Guidance for drawing out the shapes of the internal thighs
1. Cucumber
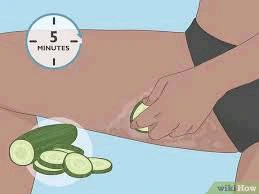
Subsequent to cutting your cucumber, quickly apply the uncovered tissue of the cucumber to the impacted locale and let it there for a couple of moments prior to washing it off with water. On the off chance that you need the best impacts conceivable from this training, you ought to perform it two times per day, once in the first part of the day and once in the prior night heading to sleep. Your skin will indeed resemble being sound. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
2. A piece of the strip of an orange
Notwithstanding the notable job that it plays as a fading specialist, the strip of an orange can likewise be used as an exfoliant for the skin. To make a glue out of the orange strip, you should simply accept the strip, permit it to dry totally prior to crushing it, and afterward join the ground strip with some honey and water. Presto! You currently have a glue out of the orange strip.
You ought to wash this glue off after first applying it to the impacted locale, allowing it to sit for a couple of moments, and afterward eliminating it from the impacted region. Continuously do your exercises in this design consistently.
3. Aloe vera is one more kind of normal fixing that can ease up the skin. Subsequent to cutting the aloe vera plant fifty, scratch the gel out of the center of the plant, and apply it to the area that should be peeled. Subsequent to saving it for a couple of moments, you ought to give the locale a total cleaning.
4. Lime
Lemon, similar to orange, can be utilized to shed the skin; essentially apply the juice to your skin and wash it off following a couple of moments. Orange is one more natural product that can be utilized in a similar way. Orange is one more organic product that can be used in a similar way as recently portrayed.
5. Tomatoes.
In the wake of cutting a tomato down the middle and applying the juice to the impacted region, clean up following a couple of moments have passed. Tomatoes are a characteristic solution for an assortment of skin conditions.

 SPORTS9 months ago
SPORTS9 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago
 SPORTS9 months ago
SPORTS9 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago