IN-THE-NEWS
How to Plant, Grow and Care for Lemongrass
Published
5 months agoon
By
1oo9t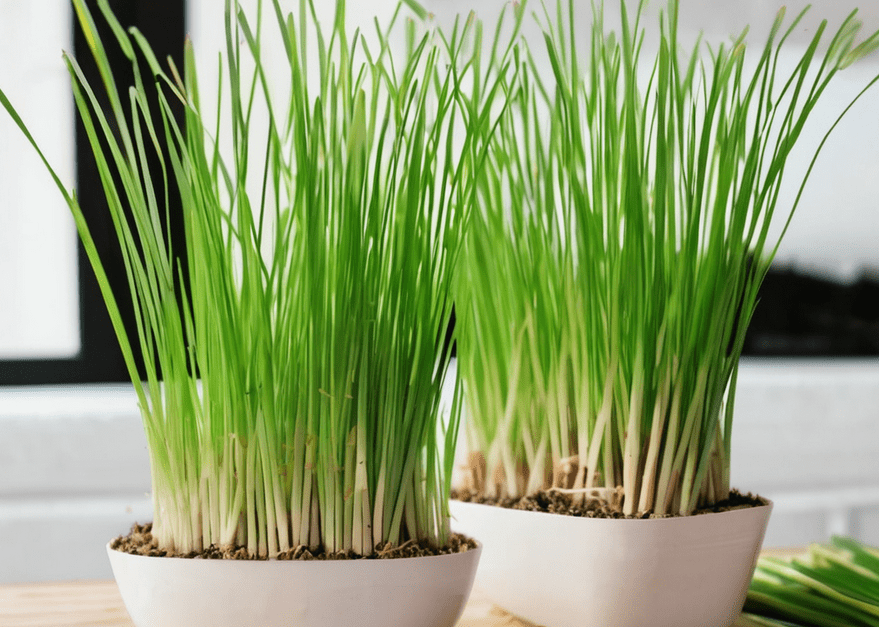
Have you ever dreamed of adding a touch of vibrant flavor to your dishes? You should try Lemongrass! Lemongrass is more than just a fragrant herb—it’s a powerhouse in both the kitchen and the garden. Its bright, citrusy aroma and flavor can transform everything from soups and curries to teas and marinades. It’s a key ingredient in many global cuisines, particularly Southeast Asian dishes.
Plus, it’s easy to grow at home with just a little care and attention. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about planting, growing, and caring for lemongrass. We’ll also explore how to incorporate this versatile herb into your cooking to make the most of your harvest…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
What is Lemongrass?
Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) is a tropical plant that belongs to the grass family. It’s known for its strong citrus aroma and flavor, which it gets from essential oils found in its long, slender stalks. Lemongrass is most commonly associated with Asian cuisine—particularly Thai, Vietnamese, and Indian dishes. Plus, it’s also used in herbal teas, as a natural insect repellent, and for medicinal purposes.
Lemongrass grows in clumps of grass-like stalks that can reach up to 3 feet tall, depending on the variety and growing conditions. It’s known for its ability to thrive in warm climates. This makes it ideal for outdoor gardening in many regions. However, with the right care, it can also be successfully grown indoors.
Benefits of Growing Lemongrass
Before you dive into the planting process, it’s helpful to understand the many benefits that come with growing lemongrass. Here are just a few:
- Fresh Flavor Year-Round: There’s nothing quite like the taste of fresh lemongrass. Growing your own gives you an endless supply of fragrant herbs, perfect for your kitchen creations.
- Low Maintenance: Lemongrass is one of the easier herbs to grow, requiring minimal effort once established. It’s perfect for beginners or anyone looking for a low-maintenance garden addition.
- Natural Pest Control: The strong lemony scent of lemongrass is known to repel mosquitoes and other common garden pests. This makes it a great companion plant in the garden or on your patio.
- Health Benefits: Lemongrass is packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and essential oils. It’s often used in natural remedies for digestion, relaxation, and even skincare. Some people use lemongrass oil in aromatherapy for stress relief.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Lemongrass adds a lovely, ornamental element to any garden or indoor space with its tall, elegant green stalks.
Now that you know the benefits, let’s get to the fun part—planting!
Where to Grow Lemongrass?
Lemongrass thrives in warm, sunny environments, and it loves heat and humidity. Whether you live in a temperate or tropical climate, here’s what you need to know about choosing the best spot for your lemongrass plant.
Growing Lemongrass Outdoors
- Sunlight: Lemongrass needs plenty of sunlight to grow strong and healthy. Aim for at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight each day. This is why it thrives in tropical climates and summer months in temperate zones.
- Soil: Lemongrass prefers well-draining, slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0 to 7.0). The soil should be rich in organic matter to provide the nutrients it needs for strong growth. If your soil is heavy clay, consider amending it with compost to improve drainage.
- Climate: Lemongrass does best in USDA hardiness zones 9 through 11. It can handle short periods of cold, but it’s sensitive to frost and should be brought indoors or covered during the winter months if grown outside in colder climates.
Growing Lemongrass Indoors
- Containers: If you’re in a colder climate or simply want to grow lemongrass indoors, containers are your best bet. Choose a large pot (at least 12 inches in diameter) with good drainage holes. This will help prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
- Lighting: Lemongrass thrives in bright, direct sunlight. Place your container on a sunny windowsill or near a south- or west-facing window. If your space doesn’t get enough natural light, you can use a grow light to supplement.
- Temperature: Lemongrass does best in temperatures between 65°F and 85°F (18°C to 29°C). Keep it away from drafts, air conditioners, or heaters that could cause temperature fluctuations.
How to Plant Lemongrass?
There are two main ways to plant lemongrass: from seed or cutting. Let’s take a closer look at both options.
Starting Lemongrass from Seed
While starting from seed is possible, it’s a slower process and may take several weeks for the seeds to germinate. Here’s how to do it:
- Prepare the Soil: Use a seed-starting mix in a shallow container with good drainage. Lemongrass seeds are tiny, so avoid burying them deeply in the soil. Just press them gently into the surface.
- Soak the Seeds: For quicker germination, soak the seeds in warm water for about 1–2 hours before planting. This helps to soften the seed coat and speeds up the sprouting process.
- Keep the Soil Moist: After sowing, lightly mist the soil with water to keep it moist. Germination usually takes 2–3 weeks.
- Transplanting: Once the seedlings have grown large enough to handle (around 6–8 inches tall), transplant them into larger containers or your garden.
Starting Lemongrass from a Cutting (Recommended)
The most reliable way to propagate lemongrass is from a cutting, which can be done with a fresh stalk from a grocery store or a nursery. Here’s how:
- Choose a Fresh Stalk: Look for firm, healthy lemongrass stalks with vibrant green leaves and no signs of decay.
- Cut the Stalk: Trim a 4-6 inch piece from the bottom of the stalk, making sure to leave the base intact. This is the part that will sprout roots.
- Place in Water: Submerge the cut end of the stalk in a jar or glass of water, ensuring the bottom portion is underwater. Place it in a warm spot with indirect light.
- Wait for Roots to Form: Within a week or two, you should notice roots developing. Once the roots are about 2-3 inches long, it’s time to plant your lemongrass in soil.
- Plant in Soil: Transplant the rooted stalk into a pot or garden bed with rich, well-draining soil. Water it thoroughly and continue caring for it as it grows.
How often should I water lemongrass?
Lemongrass likes consistent moisture but doesn’t want to sit in water. Water it regularly to keep the soil evenly moist, especially during hot months. However, make sure the soil drains well, as standing water can cause root rot. During colder months, you can water less frequently, but always check the soil moisture before watering.
What type of soil is best for lemongrass?
Lemongrass prefers well-draining, slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0-7.0). A loamy soil with organic matter works best, as it provides good drainage while retaining moisture. If you’re planting in a garden, amend the soil with compost to improve texture and nutrient levels. For container gardening, you can use a high-quality potting mix.
How long does lemongrass take to grow?
If you’re growing lemongrass from a cutting, it can take about 2-3 weeks for the roots to develop. Once transplanted into the soil, it can take about 2-3 months to reach a harvestable size, depending on growing conditions like sunlight, temperature, and care.
Can I grow lemongrass from seed?
Yes, you can grow lemongrass from seed, but it’s typically a slower process compared to starting from a cutting. Lemongrass seeds take around 2-3 weeks to germinate, and it may take longer to reach a harvestable size. If you’re looking for a faster method, starting with a cutting from a store-bought stalk is recommended.
Does lemongrass need a lot of sunlight?
Yes, lemongrass needs full sunlight to grow well. Ideally, it should get at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight each day. If you are growing it indoors, place it on a sunny windowsill that receives plenty of light, or consider using artificial grow lights if necessary.
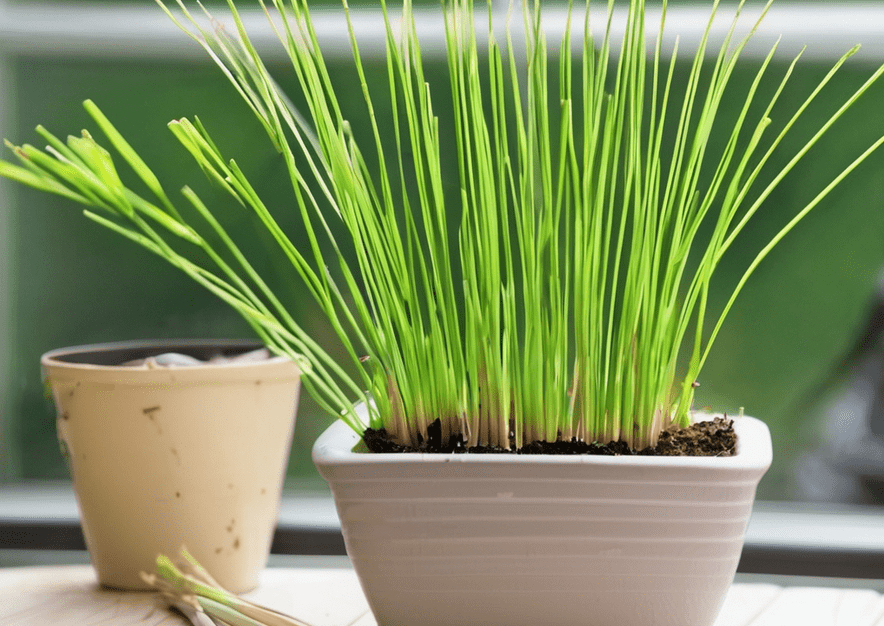

How to Care for Lemongrass?
Once your lemongrass is planted, it’s time to take care of it. Lemongrass is a relatively low-maintenance plant, but it does have some specific needs.
1. Watering
Lemongrass likes consistent moisture but doesn’t want to sit in water. Water it regularly, ensuring that the soil stays evenly moist, but not soggy. Be sure to water it deeply to encourage strong root growth. During hotter months, you may need to water it every 2-3 days; in cooler weather, once a week is usually enough.
2. Fertilizing
To keep your lemongrass growing strong and healthy, fertilize it every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer). A balanced, slow-release fertilizer works well. You can also use organic compost to enrich the soil. Avoid fertilizing in the winter when the plant is dormant. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
3. Pruning and Maintenance
Lemongrass grows in a clump, and it can get quite tall. Regular pruning helps to keep the plant healthy and encourages new growth. Here’s how to do it:
- Remove Dead Leaves: Trim off any yellow or dead leaves to keep the plant looking neat and healthy.
- Cut the Stalks: If your lemongrass becomes too tall or unruly, trim back the outer stalks. Always leave the inner clump of stalks intact, as this is where new growth will emerge.
- Check for Flowers: Lemongrass can sometimes produce flower heads, but these should be removed to prevent the plant from becoming leggy.
How can I fix root rot in lemongrass?
Root rot typically occurs when the plant is overwatered or the soil does not drain well. To fix this, remove the plant from the pot or garden bed, inspect the roots, and trim away any brown or mushy parts. Report it in fresh, well-draining soil, and adjust your watering schedule to avoid overwatering in the future.
What pests affect lemongrass, and how do I get rid of them?
Lemongrass can attract pests such as aphids, mealybugs, and spider mites. To treat these, you can spray the plant with a mixture of water and mild dish soap or neem oil, which is a natural insecticide. If the infestation is severe, you may need to repeat the treatment every few days until the pests are gone.
Does lemongrass need to be pruned?
Yes, lemongrass benefits from regular pruning. Remove any dead or yellowing leaves to keep the plant healthy and looking neat. You can also trim the outer stalks if the plant gets too tall or unruly. Always leave the inner stalks intact so the plant can continue to grow.
How do I store fresh lemongrass?
Fresh lemongrass can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a week. Simply wrap the stalks in a damp paper towel and place them in a plastic bag. If you have a large harvest, you can also freeze lemongrass for longer storage. Just cut the stalks into 2-3 inch pieces and freeze them in an airtight container or freezer bag.
Can I use dried lemongrass instead of fresh?
Yes, you can use dried lemongrass in cooking, although fresh lemongrass provides a more intense, aromatic flavor. If using dried lemongrass, you may need to increase the amount in your recipe to compensate for the less potent flavor. Dried lemongrass is particularly good for making tea or adding to slow-cooked dishes.
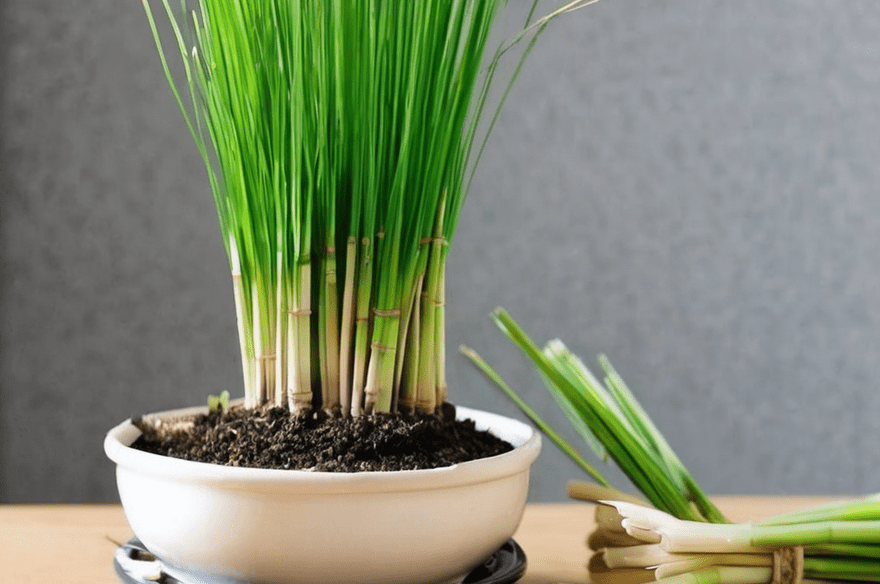

Common Lemongrass Problems and How to Fix Them
Like any plant, lemongrass can face a few challenges. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
1. Yellowing Leaves
Yellow leaves often indicate overwatering or a nutrient deficiency. Make sure the soil drains well, and avoid letting the plant sit in water. If the soil seems depleted, feed the plant with a balanced fertilizer or compost.
2. Pests
Lemongrass can attract pests like aphids, mealybugs, and spider mites. To control these pests, spray the plant with a mixture of water and mild dish soap or use neem oil.
3. Root Rot
If you notice wilting or mushy leaves, root rot may be the issue. This happens when the plant sits in waterlogged soil. Ensure your container or garden bed has proper drainage, and allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
How to Harvest Lemongrass?
Lemongrass is ready to harvest once it has reached a height of about 12 inches or when the stalks feel firm and full. Here’s how to harvest:
- Cut the Stalks: Using a sharp knife or scissors cut the outermost stalks at the base of the plant. Always leave the inner stalks intact to allow the plant to continue growing.
- Harvesting Frequency: Lemongrass can be harvested multiple times throughout the growing season. Be sure to leave enough stalks for the plant to regenerate.
- Best Time to Harvest: The best time to harvest lemongrass is in the morning, before the sun is too hot, as the plant’s essential oils will be at their peak.
How to Use Lemongrass in the Kitchen?
Now that you’ve grown your lemongrass, it’s time to enjoy the fruits of your labor! Here are some delicious ways to use fresh lemongrass:
- Tea: Simply bruise a stalk with the back of a knife and steep it in hot water for a fragrant and soothing tea.
- Soups and Curries: Lemongrass adds a fresh, citrusy flavor to soups, stews, and curries. Slice or bruise the stalks and add them to the dish while it’s cooking. Remove them before serving.
- Marinades: Lemongrass pairs wonderfully with garlic, ginger, and soy sauce for a flavorful marinade for meats, tofu, or vegetables.
- Infused Oils and Sauces: You can infuse oils or create sauces with lemongrass for added depth of flavor in your cooking.
Is lemongrass safe to consume?
Yes, lemongrass is completely safe to consume. It’s widely used in cooking and is also used in herbal medicine. However, if you are using lemongrass for medicinal purposes, consult a healthcare professional to ensure it’s appropriate for your needs, especially if you are pregnant or taking medications.
FAQs
1. Can lemongrass grow in cold climates?
Lemongrass is a tropical plant and does not tolerate frost. If you live in a cold climate, you can still grow lemongrass in containers and bring it indoors during the winter months. Alternatively, you can grow it in a greenhouse or indoors year-round as long as it gets enough light and warmth.
2. How big does lemongrass grow?
Lemongrass can grow quite large, with some varieties reaching up to 3 feet in height. It grows in dense clumps of long, grass-like stalks, which can spread outwards if left unchecked. Pruning can help keep it manageable and encourage new growth.
3. Can I regrow lemongrass from the kitchen?
Yes, you can regrow lemongrass from a store-bought stalk! Simply place the bottom portion of the stalk in water, and after a couple of weeks, it will begin to sprout roots. Once the roots are a few inches long, transplant them into the soil. This is a great way to start a lemongrass plant with minimal cost.
Related
You may like
IN-THE-NEWS
Why’ Donald Trump wore blue suit at Pope’s funeral as he’s slammed for having ‘no respect –
Published
1 day agoon
May 8, 2025By
1oo9t
Religious and political leaders from all over the world came together on Saturday, April 26, for the funeral of Pope Francis. One thing that caught a lot of attention was Donald Trump’s choice of clothing. Many people were shocked and upset because Trump showed up wearing a blue suit, while it is normally expected for people to wear black to a funeral as a sign of respect and mourning.
At funerals, especially ones as significant as a Pope’s, the tradition is to wear black. It shows that you are honoring the life of the person who passed away and sharing in the sadness. So, it would be natural to expect everyone at the Vatican that day to stick to this tradition.
However, Trump, who recently returned to office, wore a blue suit. His wife, Melania Trump, followed the tradition and dressed in black, even though it was her 55th birthday. People online quickly noticed and began criticizing Trump for what they saw as disrespectful behavior. Many accused him of breaking the funeral’s dress code and showing a lack of class…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
One person asked why Trump didn’t wear black like everyone else. Another said that while watching the funeral coverage on BBC News, they noticed Trump standing out in his blue suit while everyone around him wore black, calling it a sign of “no class.” Someone else simply said Trump showed “no respect.”
To be fair to Trump, he wasn’t the only person who chose to wear blue. Prince William and Indian President Droupadi Murmu also wore blue suits. This suggests that there might have been a reason behind their choice, and that it wasn’t just Trump trying to be different or disrespectful. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
While Trump was reportedly unhappy about having a less important seat at the funeral, it turns out he wasn’t really breaking any formal rules with his clothing. Catholics have pretty clear expectations when it comes to funeral clothing—dark suits, black ties, and dark buttons on their jackets—but these rules don’t apply as strictly to people from other religions or Christian denominations. Trump identifies as a non-denominational Christian, Prince William is from the Church of England, and President Murmu is Hindu. Because they are not Catholic, they might have felt it was acceptable to wear dark blue instead of black.
Sky News explained that the suggested dress code for men attending the funeral was a dark suit with a black tie and a black button on the lapel of their jacket. A white shirt underneath was fine.
Even though Pope Francis was known for being more relaxed and open to doing things differently, it’s possible he would have hoped that Trump would at least wear a darker suit. After all, the two had clashed in the past, particularly when Pope Francis criticized Trump’s 2016 campaign idea of building a wall between the US and Mexico.
In the end, Trump’s choice to wear blue might not have been about making a statement or being disrespectful. Given that other world leaders made similar choices, it seems he had a legitimate excuse this time around, even if it didn’t sit well with everyone watching.
Related
IN-THE-NEWS
Food Allergy Symptoms + 6 Ways to Reduce Them
Published
3 days agoon
May 6, 2025By
1oo9t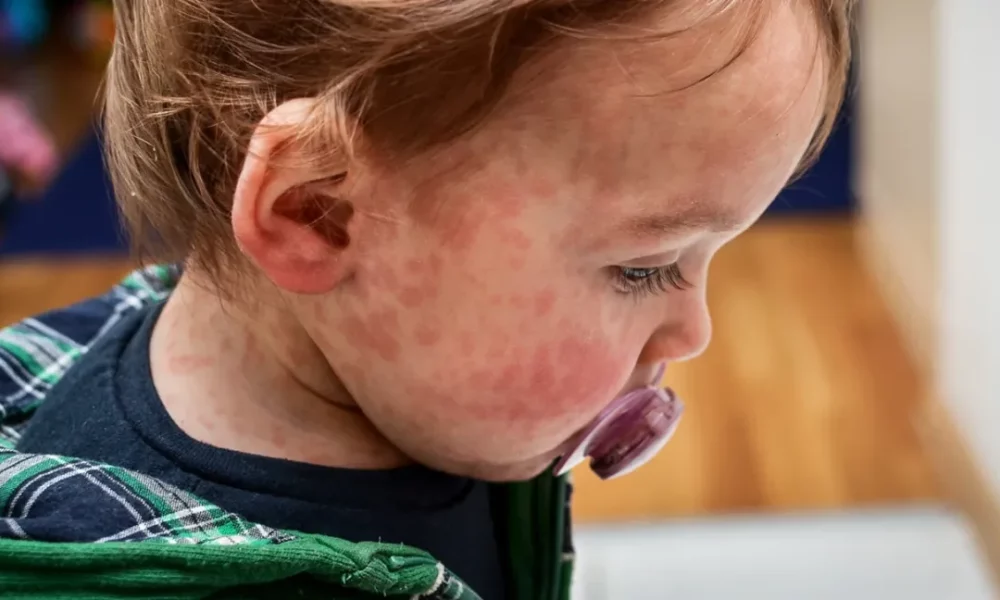
Food allergies are immune-based diseases that have become a serious health concern in the United States, with an estimated 32 million Americans dealing with food allergy symptoms according to the food allergy research organization FARE.
Despite the risk of severe allergic reactions and even death, there is no current cure for food allergies. The condition can only be managed by allergen avoidance or treatment of food allergy symptoms.
Fortunately, there are natural allergy fighters that can help boost the immune system and enhance the gut microbiota, which helps reduce the development of food allergies and food allergy symptoms…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
What Are Food Allergies?
Food allergies consist of immune system responses to disagreeable foods. The body senses that a protein in a particular food may be harmful and triggers an immune system response, producing histamine to protect itself. The body “remembers” this, and when this food enters the body again, the histamine response is more easily triggered.
The diagnosis of food allergies may be problematic because nonallergic food reactions, such as food intolerances, are frequently confused with food allergy symptoms. Intolerance derived from an immunological mechanism is referred to as a food allergy, and the non-immunological form is called a food intolerance.
Food allergies and intolerances are often linked, but there’s a clear difference between the two conditions.
A food allergy comes from a reaction of the allergen-specific immunoglobulin E antibody that is found in the bloodstream. Non-IgE-mediated food allergies are also possible. This happens when someone is exposed to a food that causes signs and symptoms of an allergy, such as allergic contact dermatitis.
A food intolerance is an adverse reaction to foods or food components but not due to immunologic mechanisms.
For example, a person may have an immunologic response to cow’s milk because of the milk’s protein, or that individual may be intolerant to milk due to an inability to digest the sugar lactose. The inability to digest lactose leads to excess fluid production in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in abdominal pain and diarrhea. This condition is termed lactose intolerance because lactose in not an allergen, as the response is not immune-based.
Food intolerances are nonspecific, and the symptoms often resemble common medically unexplained complaints, such as digestive issues.
IgE-medicated food allergies are the most common and dangerous of adverse food reactions. They cause your immune system to react abnormally when exposed to one or more specific foods. Immediate reactions to IgE-mediated food allergies are caused by an allergen-specific immunoglobulin E antibody that floats around in the bloodstream.
When IgE is working properly, it identifies triggers that could be harmful to the body, such as parasites, and tells the body to release histamine. Histamine causes allergy symptoms, such as hives, coughing and wheezing.
Sometimes IgE reacts to normal proteins that are found in foods — and when the protein is absorbed during digestion and enters the bloodstream, the entire body reacts as if the protein is a threat. This is why food allergy symptoms are noticeable in the skin, respiratory system, digestive system and circulatory system.
According to a 2014 comprehensive review published in Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology, the prevalence of food allergies in infancy is increasing and may affect up to 15 percent to 20 percent of infants. Researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine suggest that food allergies affect as many as 6 percent of young children and 3 percent to 4 percent of adults.
Updated reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 6.2 percent of adults in the U.S. have food allergies, while 5.8 percent of children do.
Researchers suggest that this increase in the prevalence of food allergies may be due to a change in the composition, richness and balance of the microbiota that colonize the human gut during early infancy. The human microbiome plays a vital role in early-life immune development and function. Since IgE-mediated food allergies are associated with immune dysregulation and impaired gut integrity, there is substantial interest in the potential link between gut microbiota and food allergies.
Common Food Allergies
Although any food can provoke a reaction, relatively few foods are responsible for a vast majority of significant food-induced allergic reactions. Here are some of the most common food allergies.
1. Cow’s Milk
Cow’s milk protein allergy affects 2 percent to 7.5 percent of children. Persistence in adulthood since tolerance develops in more than 99 percent of children by age 6.
Numerous milk proteins have been implicated in allergic responses, and most of these have been shown to contain multiple allergenic epitopes (targets that an individual target binds to). IgE-mediated reactions to cow’s milk are common in infancy and non-IgE-mediated reactions are common in adults.
A 2005 study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition suggests that the prevalence of self-diagnosed cow’s milk allergy is 10fold higher than the clinically proven incidence, suggesting that a sizable population is unnecessarily restricting dairy products (for allergy purposes). READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
2. Eggs
After cow’s milk, hen egg allergy is the second most common food allergy in infants and young children. A 2012 meta-analysis of the prevalence of food allergies estimated that egg allergy affects 0.5 percent to 2.5 percent of young children.
Allergy to eggs usually presents itself in the second half of the first year of life, with a median age of presentation of 10 months. Most reactions occur upon a child’s first known exposure to egg, with eczema the most common symptom.
Five major allergenic proteins from the egg of the domestic chicken have been identified, the most dominant being ovalbumin.
3. Soy
Soy allergy affects approximately 0.4 percent of children. According to a 2010 study conducted at John Hopkins University School of Medicine, 50 percent of children with a soy allergy outgrew the allergy by 7 years old.
Prevalence of sensitization after the use of soy-based formulas is around 8.8 percent. Soy formula is commonly used for infants who are allergic to cow’s milk, and research suggests that soy allergy occurs in only a small minority of young children with IgE-associated cow’s milk allergy.
4. Wheat
Gluten-related disorders, including wheat allergy, celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, have an estimated global prevalence close to 5 percent. These disorders share similar symptoms, making it difficult to make a clear diagnosis.
A wheat allergy represents a type of adverse immunologic reaction to proteins contained in wheat and related grains. IgE antibodies mediate the inflammatory response to several allergenic proteins found in wheat. Wheat allergy affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract.
Wheat allergy shows greater prevalence in children who commonly outgrow the allergy by school age.
5. Peanuts
Peanut allergy tends to present itself early in life, and affected individuals generally do not outgrow it. In highly sensitized people, just trace quantities of peanuts can induce an allergic reaction. Research suggests that early exposure to peanuts may reduce the risk of developing a peanut allergy.
According to a 2010 study, peanut allergy affects approximately 1 percent of children and 0.6 percent of adults in the U.S. Peanuts are inexpensive and frequently eaten in unmodified form and as components of many different prepared foods. They cause the largest number of cases of severe anaphylaxis and death in the U.S.
6. Tree Nuts
The prevalence of tree nut allergies continues to increase worldwide, affecting about 1 percent of the general population. These allergies begin most often during childhood, but they can occur at any age.
Only about 10 percent of people outgrow tree nut allergies, and frequent lifetime reactions caused by accidental ingestion are a serious problem.
Nuts that are most commonly responsible for allergic reactions include hazelnuts, walnuts, cashews and almonds. Those that are less frequently associated with allergies include pecans, chestnuts, Brazil nuts, pine nuts, macadamia nuts, pistachio, coconut, Nangai nuts and acorns.
A 2015 systematic review found that walnut and cashew allergies were the most prevalent types of tree nut allergy in the U.S.
7. Fish
According to a study published in Clinical Reviews of Allergy and Immunology, adverse reactions to fish are not only mediated by the immune system causing allergies, but are often caused by various toxins and parasites, including ciguatera and anisakis. (See the list of fish you should never eat.) Allergic reactions to fish can be serious and life-threatening, and children usually don’t outgrow this type of food allergy.
A reaction is not restricted to the ingestion of fish, as it can also be caused by handling fish and intaking the cooking vapors. Prevalence rates of self-reported fish allergy range from 0.2 percent to 2.29 percent in the general population but can reach up to 8 percent among fish processing workers.
8. Shellfish
Allergic reactions to shellfish, which comprises the groups of crustaceans (such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, woodlice and barnacles) and molluscs (such as squid, octopus and cuttlefish), can cause clinical symptoms ranging from mild urticaria (hives) and oral allergy syndrome to life-threatening anaphylactic reactions.
Shellfish allergy is known to be common and persistent in adults, and it can cause anaphylaxis in both children and adults. The prevalence of shellfish allergy is anywhere from 0.5 percent to 5 percent. Most shellfish-allergic children have sensitivity to dust mite and cockroach allergens as well.
A phenomenon called cross-reactivity may occur when an antibody reacts not only with the original allergen, but also with a similar allergen. Cross-reactivity occurs when a food allergen shares structural or sequence similarity with a different food allergen, which may then trigger an adverse reaction similar to that triggered by the original food allergen.
Related

In the shadowy underbelly of the ongoing War on Drugs, a chilling narrative unfolds – one that lays bare the grim realities of the drug trade and the heart-wrenching consequences it leaves in its wake.
At the epicenter of this dark and twisted saga stand figures like Dexter Lee Williams, whose actions etch a haunting reminder of the depths to which humanity can plummet when ensnared by the tantalizing allure of power and profit.
Against the backdrop of history’s notorious drug lords, such as El Chapo and Pablo Escobar, Williams solidifies his name as a haunting presence, orchestrating a vast and malevolent drug ring that casts a long, ominous shadow over the city of Atlanta, Georgia.
The saga unravels over a span of five tumultuous years, punctuated by law enforcement’s relentless pursuit and unwavering resolve to dismantle the sprawling drug empire. Wiretaps weave a damning tapestry of incriminating conversations, recorded phone calls that reverberate with the sinister whispers of a nefarious criminal network…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
A symphony of arrests unfolds, each connected strand leading inexorably to one central figure – Baxter Lee Williams. It doesn’t take a seasoned sleuth to discern that Williams’ criminal past is far from pristine, with prior arrests for cocaine and marijuana distribution foreshadowing the malevolent undertones that have always permeated his existence.
Yet, Williams seems driven by an insatiable desire to transcend the boundaries of a mere small-time operator, to ascend the ranks to the echelons of a formidable drug kingpin. This grim trajectory climaxes in March 2020, a pivotal moment that echoes the crescendo of his criminal pursuits.
Authorities intercept a colossal shipment, containing a staggering 87 pounds of cocaine – a haul valued at nearly four million dollars. This seizure serves as a potent reminder of the seismic impact of Williams’ operations, an abrupt departure from the minor infractions that previously marked his criminal escapades.
As Williams finds himself ensnared within the relentless grasp of the law, a hallowed courtroom metamorphoses into a stage for his reckoning. The judge’s voice reverberates with gravity, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of the drug trade and the grave peril it poses to the community at large.
Williams, resolute yet undoubtedly apprehensive, absorbs the full weight of his actions as his attorney endeavors to mount a defense. Amidst this legal tableau, the echoes of his past crimes reverberate, building to a crescendo that culminates in a sentence that will rob him of his liberty for the next four decades.
Each sentence pronounced in the courtroom underscores the unyielding gravity of drug-related offenses, painting a stark portrait of the devastating consequences that accompany such actions. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
The judge’s words serve as an unwavering reminder that society will not tolerate the degradation of its very fabric. In the midst of this legal maelstrom, Wallace Bigger emerges as a figure whose journey from drug network operator to defendant unveils a sordid tapestry of crime, substandard operations, and a brazen disregard for the lives ensnared by his machinations.
Within the confines of the courtroom, the judge’s gaze bores into Bigger, a man who has boldly navigated the shadowy underbelly of the drug trade. The judge’s stern commentary on Bigger’s lifestyle underscores the dire choices he has made, as well as the lives forever altered by his actions.
The judge’s words echo with a resounding admonishment – Bigger’s actions were far from inconsequential, and the consequences will reverberate throughout the annals of history.
The courtroom’s theater unfolds further as Benjamin Bundy steps into the spotlight, a name that evokes chilling echoes of the infamous serial killer, Ted Bundy. In a poignant moment, tears cascade down Bundy’s face as he grapples with the gravity of the lives lost due to his actions. The weight of guilt hangs heavy in the air, a marked contrast to the audacity that characterized his criminal enterprise.
Amidst the courtroom drama, moments of anguish and heartbreak pierce through the veneer of criminality. The families of the victims lay bare their pain, their voices quivering with raw emotion. In the face of such palpable grief, Bundy’s veneer of stoicism crumbles, giving way to tears and a vulnerability that belies the ruthlessness of his actions. The courtroom becomes a battleground of emotions, a space where the intersection of justice and personal tragedy paints a poignant tableau.
In the grim world of drug lords, Charles Crusty emerges as a figure that defies conventional categorization. Operating as a real-life Kingpin, he weaves a sinister tapestry of violence and manipulation, forcing addicts into a nightmarish servitude through brutality and fear. The judge’s condemnation of Crusty’s actions pierces the courtroom, casting a stark light on the twisted web he has spun. The judge’s words leave little room for ambiguity – Crusty’s actions will bear consequences that reverberate for generations to come.
In a world marred by the darkest facets of humanity, the courtroom stands as a crucible of accountability. Whether it is Dexter Lee Williams, Wallace Bigger, Benjamin Bundy, or Charles Crusty, their journey through the legal labyrinth is a testament to the inexorable pursuit of justice.
Within the courtroom’s hallowed halls, the voices of victims and perpetrators interweave, forming a tapestry of raw emotion, palpable consequence, and the unending struggle to grapple with the enigmatic forces of criminality that threaten to consume us all.
Related
Trending
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoTV ratings: Euro football final far ahead of Paris concert
-

 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE10 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE10 months agoWhy Hair Grows On Our Ears As We Age
-

 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months agoIf You Don’t Want To Suffer Stroke At Old Age, Avoid Excess Intake Of These 3 Things
-
SPORTS9 months ago
Atlanta Falcons’ Rondale Moore Placed on Injured Reserve Due to Season-Ending Knee Injury
-

 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months agoSerie A Clubs Can Learn from Spain’s Euro 2024 Success, Says Former Coach Arrigo Sacchi
-

 IN-THE-NEWS10 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS10 months agoThree-Year-Old Child Dies After Falling Into An Open Cesspit In Lagos
-
 HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months ago
HEALTH & LIFESTYLE5 months agoDo This If a Fish Bone Enters Your Throat, Don’t Panic Do These Things To Save Your Life
-

 SPORTS9 months ago
SPORTS9 months agoBadosa’s Winning Streak Snapped by Ostapenko in Toronto: A Hard-Fought Battle Ends in Disappointment
