Have you ever experienced a ringing, buzzing, hissing, or whistling sound in your ears, even when there is no external noise source? This phenomenon, known as tinnitus, can be annoying and sometimes worrying. Tinnitus is not a condition itself but rather a symptom of an underlying issue. While it can be temporary or chronic, understanding the potential causes can help you determine the appropriate course of action. In this article, we’ll explore 10 possible reasons for ringing ears and what you can do about it.
1. Exposure to Loud Noises
One of the most common causes of tinnitus is exposure to loud noises. Prolonged exposure to loud music, machinery, or other loud environments can damage the tiny hair cells in your inner ear, leading to ringing or buzzing sensations. This type of tinnitus is often temporary and may go away once you remove yourself from the loud environment. However, repeated or prolonged exposure can cause permanent damage and chronic tinnitus.
What to do: If you work or engage in activities that expose you to loud noises, it’s essential to wear proper ear protection, such as earplugs or noise-canceling headphones. Additionally, try to limit your exposure to loud sounds and give your ears a break from time to time.
2. Age-Related Hearing Loss
As we age, the tiny hair cells in our inner ears can gradually deteriorate, leading to age-related hearing loss (presbycusis). This natural process can also cause tinnitus, as the damaged hair cells may send irregular signals to the brain, leading to ringing or buzzing sounds.
What to do: If you suspect your tinnitus is related to age-related hearing loss, it’s essential to have your hearing checked by an audiologist. They can recommend appropriate treatments, such as hearing aids or sound therapy, to help manage the tinnitus and improve your overall hearing.
3. Earwax Buildup
Excessive earwax buildup can block the ear canal and cause tinnitus. When the ear canal is obstructed, it can create pressure or vibrations that lead to ringing or buzzing sounds.
What to do: If you suspect earwax buildup is causing your tinnitus, it’s best to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can safely remove the excess earwax and provide guidance on proper ear hygiene to prevent future buildup.
4. Head or Neck Injuries
Injuries to the head or neck can sometimes lead to tinnitus. Trauma to the bones in the ear or the nerve pathways involved in hearing can cause ringing or buzzing sensations.
What to do: If you’ve recently experienced a head or neck injury, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider can evaluate the extent of the injury and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include medications, physical therapy, or other interventions to help manage the tinnitus.
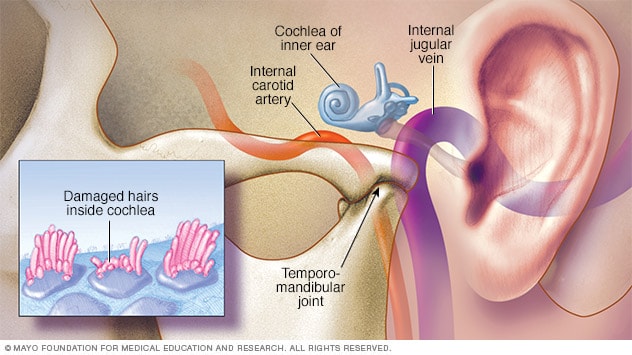
5. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the hinge that connects your jawbone to your skull. Disorders affecting this joint can cause tension or misalignment, leading to tinnitus in some cases.
What to do: If you suspect your tinnitus is related to a TMJ disorder, consult with a dentist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. They may recommend treatments such as dental splints, physical therapy, or jaw exercises to alleviate the TMJ issue and potentially reduce the ringing or buzzing sounds.
6. Ménière’s Disease
Ménière’s disease is a rare disorder that affects the inner ear and can cause tinnitus, along with vertigo (dizziness), hearing loss, and a feeling of pressure or fullness in the affected ear.
What to do: If you experience symptoms consistent with Ménière’s disease, it’s essential to seek medical attention from an ENT specialist or an audiologist. They can perform various tests to diagnose the condition accurately and recommend appropriate treatments, such as medications, dietary changes, or surgical interventions in severe cases.
7. Cardiovascular Problems
In some cases, tinnitus can be a symptom of an underlying cardiovascular problem, such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), or a tumor pressing on the blood vessels near the ear.
What to do: If you have a history of cardiovascular issues or if your tinnitus is accompanied by other symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They may order additional tests, such as blood pressure monitoring or imaging studies, to identify any underlying cardiovascular conditions and provide appropriate treatment.
8. Medications
Certain medications, including some antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antidepressants, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause tinnitus as a side effect. This is often temporary and goes away once the medication is stopped or the dosage is adjusted.
What to do: If you suspect your tinnitus is related to a medication you’re taking, consult with your healthcare provider. They may recommend adjusting the dosage or switching to an alternative medication that doesn’t cause tinnitus as a side effect. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>

9. Acoustic Neuroma
An acoustic neuroma is a non-cancerous tumor that grows on the main nerve from the brain to the inner ear. As the tumor grows, it can put pressure on the nerve and cause tinnitus, as well as hearing loss and balance issues.
What to do: If you experience tinnitus along with hearing loss or balance problems, it’s essential to seek medical attention from an ENT specialist or a neurologist. They may order imaging tests, such as an MRI, to diagnose an acoustic neuroma and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or close monitoring.
10. Stress and Anxiety
While stress and anxiety are not direct causes of tinnitus, they can exacerbate or worsen the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears. Stress and anxiety can also make it more difficult to cope with or ignore the symptoms of tinnitus.
What to do: If you believe stress or anxiety is contributing to your tinnitus, it’s essential to find healthy ways to manage these conditions. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. Additionally, seeking professional counseling or therapy can help you develop coping strategies to better manage stress and anxiety, which may alleviate or reduce the perception of tinnitus.
Regardless of the underlying cause, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe tinnitus. Your healthcare provider can help determine the root cause and recommend appropriate treatments or management strategies.
In some cases, no specific cause can be identified, and the tinnitus may be considered subjective or idiopathic (unknown cause). In these situations, there are still various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Some common treatments and management strategies for tinnitus include:
1. Sound Therapy: This involves using external sound sources, such as white noise machines, specialized tinnitus maskers, or even music, to help mask or distract from the ringing or buzzing sounds.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help you develop coping strategies and change negative thought patterns associated with tinnitus, reducing its perceived impact on your life.
3. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT): TRT combines sound therapy with counseling and education to help your brain habituate to the tinnitus sounds, making them less noticeable over time.
4. Hearing Aids: If your tinnitus is accompanied by hearing loss, wearing hearing aids can amplify ambient sounds and reduce the perception of tinnitus.
5. Medications: In some cases, medications such as antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, or specific tinnitus medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms.
6. Lifestyle Changes: Making adjustments to your lifestyle, such as avoiding exposure to loud noises, reducing stress levels, and practicing good sleep habits, can help minimize the impact of tinnitus.
It’s important to note that while there is no single cure for tinnitus, many effective management strategies exist to help you cope with the condition and improve your quality of life. Working closely with your healthcare provider and exploring various treatment options can help you find the best approach for managing your tinnitus.
Remember, tinnitus is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be frustrating and disruptive, seeking medical attention and taking proactive steps to manage your symptoms can go a long way in reducing its impact on your daily life.

 IN-THE-NEWS5 days ago
IN-THE-NEWS5 days ago
 SPORTS5 months ago
SPORTS5 months ago
 METRO5 months ago
METRO5 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS4 days ago
IN-THE-NEWS4 days ago
 SPORTS4 months ago
SPORTS4 months ago
 SPORTS5 months ago
SPORTS5 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS5 months ago