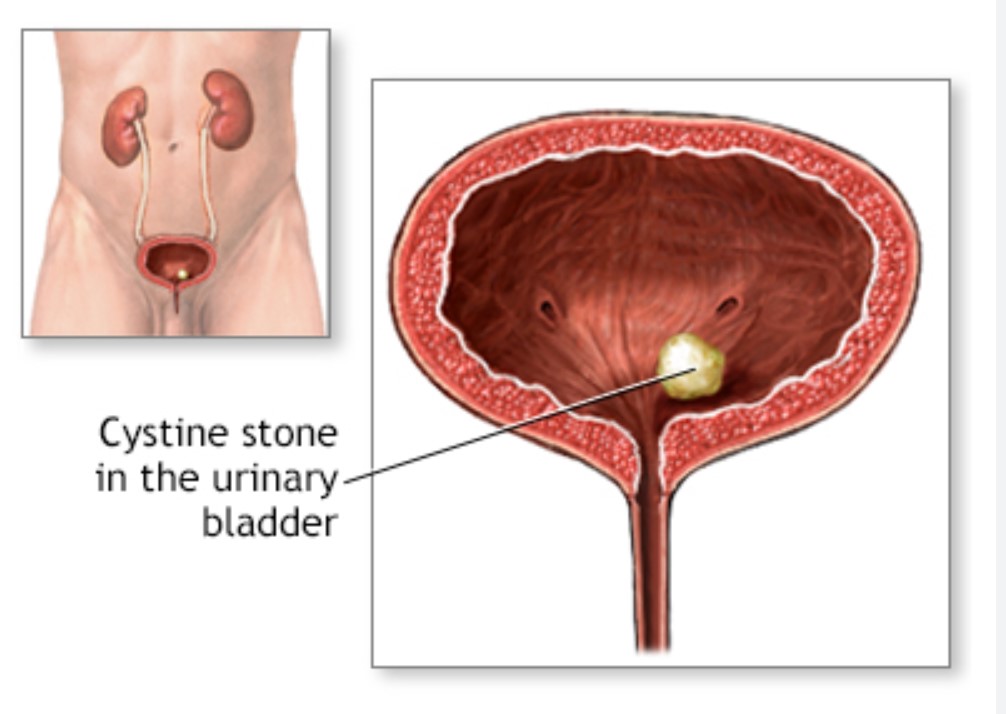
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form inside the kidneys. They can cause severe pain and other uncomfortable symptoms as they try to pass through the urinary tract. It’s important to recognize the signs of kidney stones so you can seek proper medical treatment. In this article, we’ll explore the common symptoms associated with kidney stones.
1. Severe Pain in the Back or Side
One of the most prominent symptoms of kidney stones is intense pain in the back or side, usually on one side of the body. This pain can be excruciating and may come in waves or spasms as the kidney stone moves through the urinary tract. The pain may start in the back or side and radiate toward the lower abdomen or groin area.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Kidney stones can cause nausea and vomiting, which can be triggered by the severe pain associated with the condition. The intense discomfort and pressure caused by the stone can lead to feelings of nausea and, in some cases, vomiting episodes.
3. Painful Urination
As the kidney stone moves through the urinary tract, it can cause pain or burning sensations during urination. This is because the stone can irritate or obstruct the flow of urine through the ureter (the tube connecting the kidney to the bladder) or the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body).
4. Blood in Urine
Another common symptom of kidney stones is the presence of blood in the urine, also known as hematuria. This occurs when the sharp edges of the stone scratch or irritate the delicate tissues of the urinary tract, causing bleeding. The blood in the urine may appear pink, red, or brownish in color.
5. Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine
Kidney stones can also cause changes in the appearance and odor of urine. The urine may appear cloudy or have an unusual, foul-smelling odor due to the presence of minerals, bacteria, or other substances associated with the kidney stone.
6. Frequent Urge to Urinate
Some people with kidney stones may experience a frequent and persistent urge to urinate, even when they have little or no urine to pass. This is because the stone can irritate the bladder or urinary tract, causing a constant feeling of needing to urinate.
7. Fever and Chills
In some cases, kidney stones can lead to fever and chills, especially if an infection is present. This can occur if the stone causes a blockage in the urinary tract, allowing bacteria to accumulate and cause an infection.
8. Groin or Testicular Pain (in Men)
Men with kidney stones may experience pain or discomfort in the groin or testicles. This is because the stone can irritate or obstruct the urinary tract near the bladder or prostate gland, causing referred pain in these areas.
It’s important to note that not everyone with kidney stones will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. Some people may have mild symptoms or even no symptoms at all if the stone is small and passes without causing significant obstruction or irritation. READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
If you suspect you may have kidney stones, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider will likely perform various tests, such as urine analysis, blood tests, and imaging studies (like a CT scan or ultrasound), to confirm the presence of a kidney stone and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment options for kidney stones can vary depending on the size, location, and composition of the stone, as well as the severity of symptoms. Some common treatments include:
1. Pain Management: Pain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids, may be prescribed to help manage the severe pain associated with kidney stones.
2. Increasing Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help flush out kidney stones and promote their passage through the urinary tract.
3. Medications: Certain medications, like alpha-blockers or calcium channel blockers, may be prescribed to help relax the muscles of the urinary tract and facilitate the passage of the stone.
4. Lithotripsy: This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to break down larger stones into smaller fragments that can pass more easily through the urinary tract.
5. Surgery: In some cases, minimally invasive surgical procedures, such as ureteroscopy or percutaneous nephrolithotomy, may be required to remove larger or obstructive kidney stones.
Prevention is key when it comes to kidney stones. Staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive intake of certain foods or supplements that contribute to stone formation (like oxalate-rich foods or high doses of vitamin C) can help reduce the risk of developing kidney stones.
In conclusion, kidney stones can cause a range of uncomfortable and potentially severe symptoms, including severe pain, nausea, blood in the urine, and frequent urination. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate the discomfort and prevent potential complications associated with kidney stones.

 SPORTS11 months ago
SPORTS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 SPORTS11 months ago
SPORTS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 SPORTS11 months ago
SPORTS11 months ago