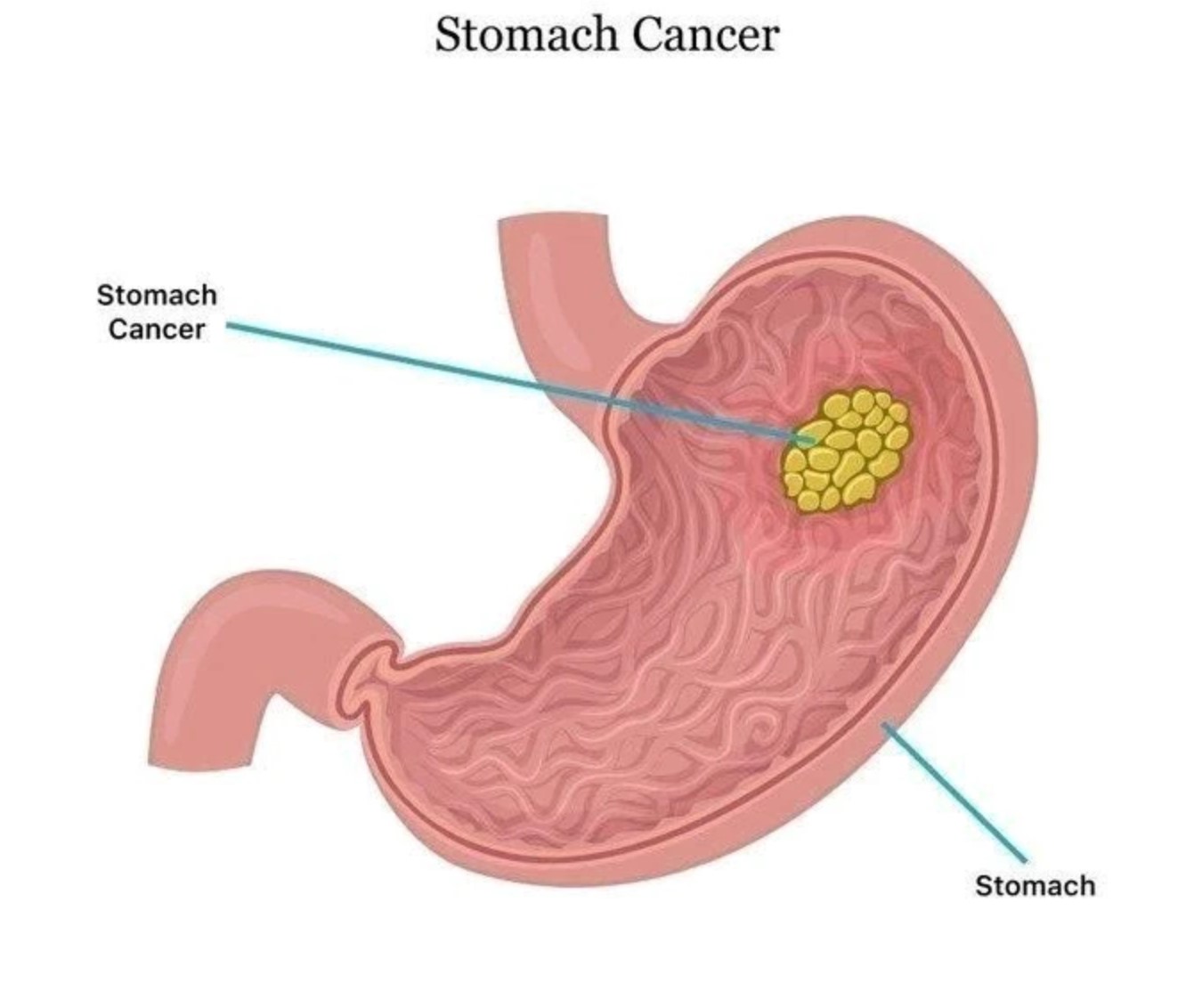
The headline “Stomach Cancer Kills Fast: Avoid Too Much Intake Of These 3 Things If You Want To Live Long” aims to grab attention with a clear message about the risks of stomach cancer and preventive measures through dietary choices. However, it’s essential to delve deeper into the context, implications, and scientific basis behind such claims.
Stomach cancer, medically known as gastric cancer, is indeed a serious health concern globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths. The severity of stomach cancer lies in its often late diagnosis and rapid progression, which underscores the importance of early detection and prevention strategies…Click Here To Continue Reading>> …Click Here To Continue Reading>>
The headline suggests that excessive intake of certain substances contributes to an increased risk of stomach cancer. While specific dietary factors can influence cancer risk, it’s crucial to distinguish between correlation and causation, as well as to consider the broader context of cancer prevention.
1. Processed and Red Meat: High consumption of processed meats such as bacon, sausages, and ham, as well as red meat like beef and lamb, has been linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including stomach cancer. This association is primarily due to compounds formed during processing or cooking, such as N-nitroso compounds and heterocyclic amines, which may damage DNA and promote cancerous growths.
2. Salty and Preserved Foods: Foods preserved by salting, pickling, or fermentation (e.g., pickled vegetables, salted fish) contain high levels of salt and nitrites/nitrates, which can react in the stomach to form carcinogenic compounds. Regular consumption of these foods has been associated with an elevated risk of stomach cancer, particularly in regions where such diets are prevalent.
3. Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption is a well-established risk factor for various cancers, including stomach cancer. Alcohol can irritate the stomach lining, leading to chronic inflammation and potentially contributing to the development of cancerous cells over time.
However, it’s essential to note that while these factors are associated with increased risk, individual susceptibility varies, and cancer development typically involves multiple factors, including genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices beyond diet, and environmental exposures.
Prevention strategies should focus on a balanced approach: READ FULL STORY HERE>>>CLICK HERE TO CONTINUE READING>>>
– Dietary Modifications: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting processed meats, salty foods, and alcohol.
– Regular Screening: Early detection through screenings like endoscopy or imaging can significantly improve treatment outcomes by catching cancer in its early stages when it’s more treatable.
– Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, avoiding smoking, and managing stress are integral parts of reducing overall cancer risk.
In conclusion, while the headline rightly highlights the seriousness of stomach cancer and the role of dietary choices in prevention, it’s crucial to approach such recommendations with a balanced understanding of the complex factors contributing to cancer development. Awareness, education, and proactive health measures are key to promoting long-term health and longevity.

 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
 SPORTS10 months ago
SPORTS10 months ago
 METRO11 months ago
METRO11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS11 months ago
 IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
IN-THE-NEWS6 months ago
 METRO10 months ago
METRO10 months ago